中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (34): 6144-6151.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.34.013
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
皮下植入生肌玉红胶原后的血管新生与瘢痕抑制
曹东阳1,姚 昶2,陈德轩2,卞卫和2,张晓清2,尹 恒3,郭檬檬1
- 1南京中医药大学2011级硕士研究生,江苏省南京市 210029;2江苏省中医院,江苏省南京市 210029;3南京中医药大学2012级博士研究生,江苏省南京市 210046
Angiogenesis and scar inhibition after subcutaneous implantation of Shengji Yuhong collagen
Cao Dong-yang1, Yao Chang2, Chen De-xuan2, Bian Wei-he2, Zhang Xiao-qing2, Yin Heng3, Guo Meng-meng1
- 1Postgraduate Student of Grade 2011, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Jiangsu Province Hospital of TCM, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Doctoral Student of Grade 2012, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210046, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
背景:前期研究显示生肌玉红胶原促进血管新生与组织愈合的疗效显著好于生肌玉红膏及单纯胶原或明胶。
目的:探察兔皮下植入生肌玉红胶原促进血管新生与修复的疗效与机制。
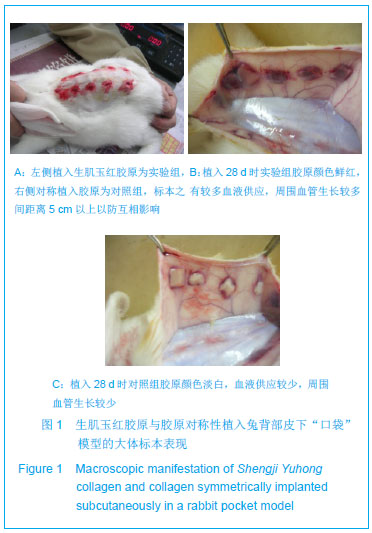
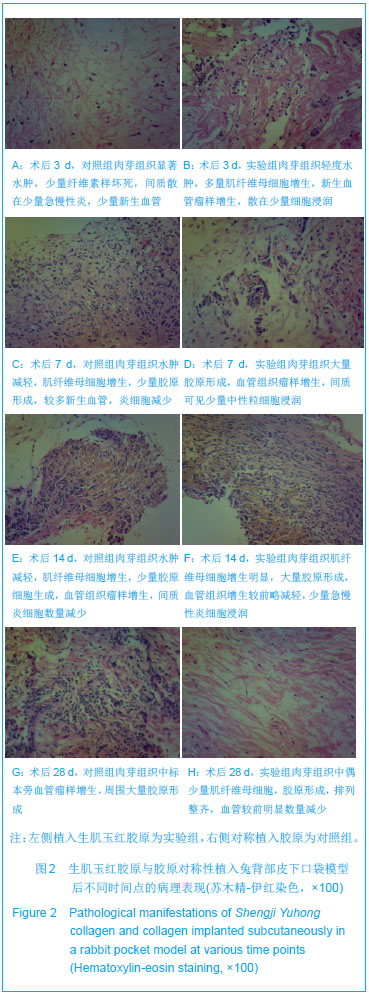
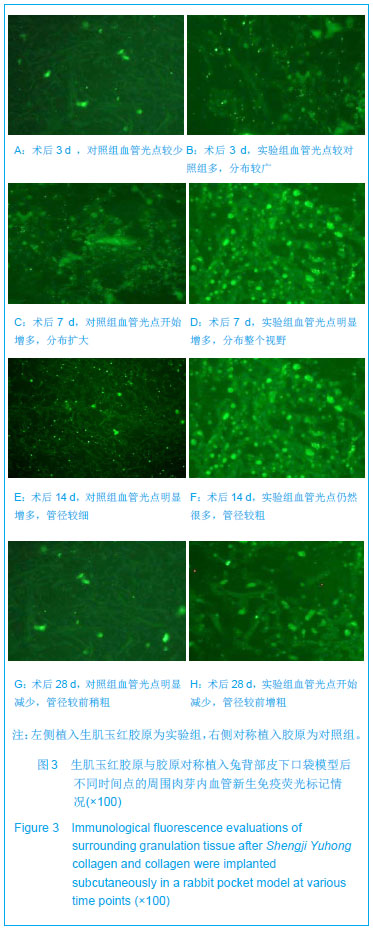
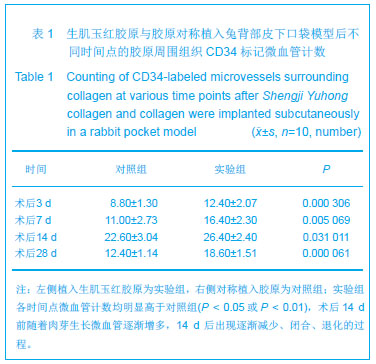
方法:在新西兰兔背部两侧对称制作皮下口袋模型,并对称植入生肌玉红胶原(实验组)与胶原(对照组),于术后3,7,14,28,56 d取植入标本及标本周围组织,制作病理切片观察标本周围组织修复状况,测定胶原内血红蛋白水平,免疫荧光与CD34 染色标记法观察周围组织微血管新生情况,Western Blot法检测血管内皮生长因子、血管生成素1的表达,免疫组织化学法观察周围组织Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原的分泌及两者的比例。
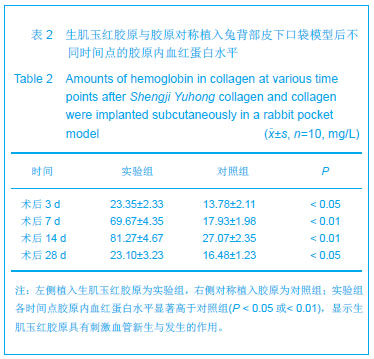
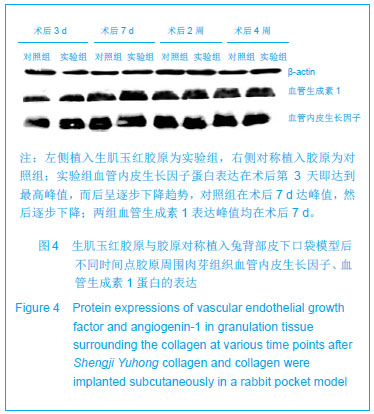
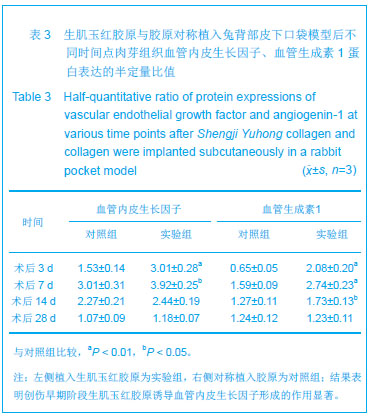
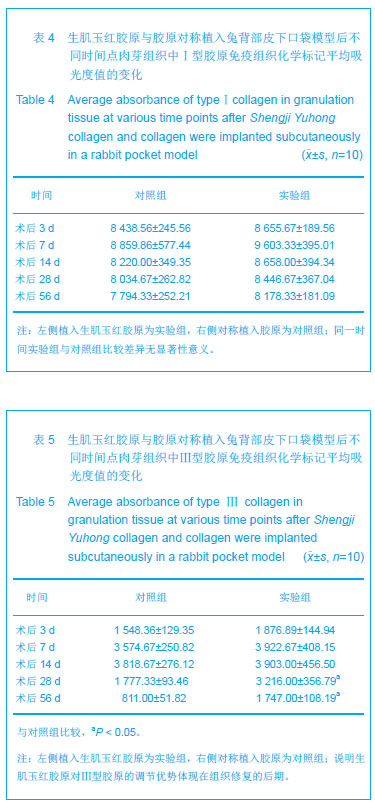
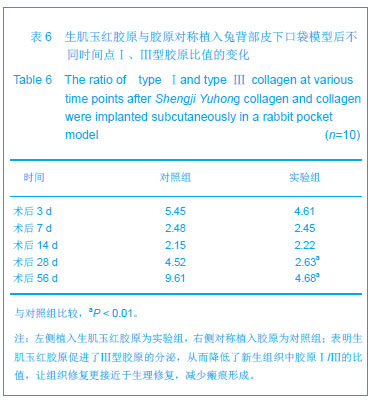
结果与结论:实验组标本周围皮下血管增多,胶原周围组织随着时间推移炎性渗出减少,肉芽组织增生,到28 d时已形成成熟的纤维结缔组织,并且促进微血管新生作用及血红蛋白水平高于对照组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),术后3,7 d血管内皮生长因子、血管生成素1表达高于对照组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);实验组Ⅰ型胶原分泌与对照组相当,但术后28,56 d Ⅲ型胶原的分泌高于对照组(P < 0.05),且术后28,56 dⅠ、Ⅲ型胶原的比例低于对照组(P < 0.01)。表明生肌玉红胶原可显著促进周围组织微血管新生,提高血管内皮生长因子与血管生成素1的表达,同时协同调节胶原形成及Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原的比例达到减少瘢痕愈合的作用。
中图分类号:
.jpg)